Ohio Medicaid Basics 2023
Published every other year since 2005, to coincide with the biennial budget process, the tenth edition of HPIO's Ohio Medicaid Basics provides an overview of the Medicaid program in Ohio, including information on Medicaid eligibility, covered services, financing, spending and recent policy and programmatic changes.
Introduction
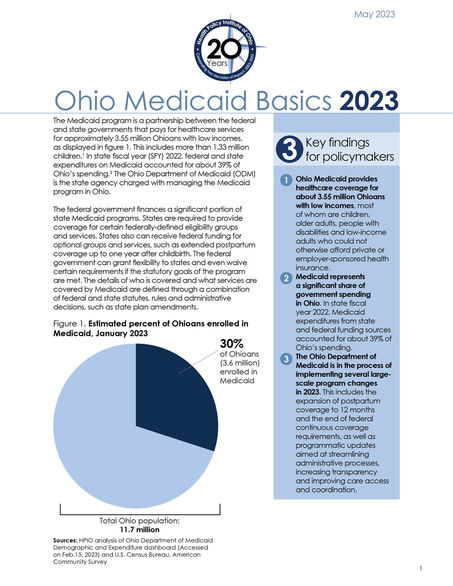
The Medicaid program is a partnership between the federal and state governments that pays for healthcare services for approximately 3.55 million Ohioans with low incomes. This includes more than 1.33 million children. In state fiscal year (SFY) 2022, federal and state expenditures on Medicaid accounted for about 39% of Ohio’s budget. The Ohio Department of Medicaid (ODM) is the state agency charged with managing the Medicaid program in Ohio.
The federal government finances a significant portion of state Medicaid programs. States are required to provide coverage for certain federally-defined eligibility groups and services. States also can receive federal funding for optional groups and services, such as extended postpartum coverage up to one year after childbirth. The federal government can grant flexibility to states and even waive certain requirements if the statutory goals of the program are met. The details of who is covered and what services are covered by Medicaid are defined through a combination of federal and state statutes, rules and administrative decisions, such as state plan amendments.
3 key findings for policymakers
- Ohio Medicaid provides healthcare coverage for about 3.55 million Ohioans with low incomes, most of whom are children, older adults, people with disabilities and low-income adults who could not otherwise afford private or employer-sponsored health insurance.
- Medicaid represents a significant share of government spending in Ohio. In state fiscal year 2022, federal and state expenditures on Medicaid accounted for about 39% of Ohio’s budget.
- The Ohio Department of Medicaid is in the process of implementing several large-scale program changes in 2023. This includes the expansion of postpartum coverage to 12 months and the end of federal continuous coverage requirements, as well as programmatic updates aimed at streamlining administrative processes, increasing transparency and improving care access and coordination.
Looking ahead
Medicaid provides coverage for healthcare services to 3.55 million Ohioans. For people who are sick or injured, access to care can mean the difference between a timely return to health or prolonged illness. For Ohioans with low incomes and chronic diseases, mental health conditions or substance use disorder, Medicaid coverage provides a means to pay for healthcare services, enabling work and active engagement in the community. Medicaid also pays for preventive services and provides a financial safety net for costs related to medical emergencies.
As Ohio continues to implement updates to the Medicaid program and undertakes the eligibility redetermination process, it will be important to pay attention to the needs of Ohioans most at risk of poor health outcomes and ensure that they are not losing critical healthcare coverage. State policymakers and other leaders should continue monitoring the outcomes of these program changes to evaluate impacts on health, equity and Medicaid spending over the next several years.
By:
Brian O’Rourke, PhD
Stephen Listisen, MPA
Édith Nkenganyi, BA
Published On
May 12, 2023
Table of Contents
 Download Publication
Download Publication
